What is Drayage: Drayage Services and Drayage Charges Explained in 2023

Drayage is a small link in the prolonged international logistics process. However, it is still significant. Freight transport, especially intermodal or multimodal transport, does not only involve vessels, airplanes, and railways but also entails drayage services to connect each part. What is drayage? How to calculate drayage fees? Is there any way to cut back on the drayage fees? Read on, and we will give you the most detailed and updated explanation about drayage.
- 1. What Does Drayage Mean in Shipping?
- 2. What is a Drayage Truck?
- 3. Why Does Drayage Play an Important Role in Freight Shipping?
- 4. What is the Difference Between Freight and Drayage?
- 5. What are the Different Types of Drayage Services?
- 6. What are Drayage Charges?
- 7. How to Calculate Drayage Charges?
- 8. Six Effective Ways to Reduce Drayage Fees
1. What Does Drayage Mean in Shipping?
Drayage stands for the transport of containerized freight or bulk cargo over a short distance. It is a part of the whole supply chain process. Using drayage services means that your goods will be delivered between different locations by trucks. And the locations vary: seaports, distribution centers, order fulfillment stations, storage lots, warehouses, rail yards, transport terminals, or even the customer's doorstep.
2. What is a Drayage Truck?
As it is mentioned above, drayage refers to a type of trucking service. The most common drayage truck type is the large semi-trailer truck. Drayage trucks are used to deliver goods (generally containers and bulk freight) from one place to another. Drayage trucks are functionally equipped to hold almost all types of containers: standard dry containers, high cube containers, and refrigerated containers. Typically, drayage trucks will only transport goods for a short haul, which can be finished within a day in most cases.
3. Why Does Drayage Play an Important Role in Freight Shipping?
The short-haul transportation of your goods by truck is a small link in the supply chain. However, drayage will determine what the first mile or the last mile of your cargo's journey looks like. And that is why drayage is important.
Drayage is a indispensable part of the intermodal shipping or multimodal shipping process. It connects different modes of transportation: rail, sea, and air. For instance, you will need to use drayage services when transferring cargo from a seaport to a rail yard in order to begin its rail transportation.
4. What is the Difference Between Freight and Drayage?
By definition, freight shipping means the transportation of goods in bulk via air, sea, or rail. In contrast, drayage is considered a small part of the larger freight shipping process. Freight can be moved in or out of the port relying on drayage services. Through drayage, the freight can be transported from one location to another, for instance, from a warehouse to a port or from a port to the end customer.
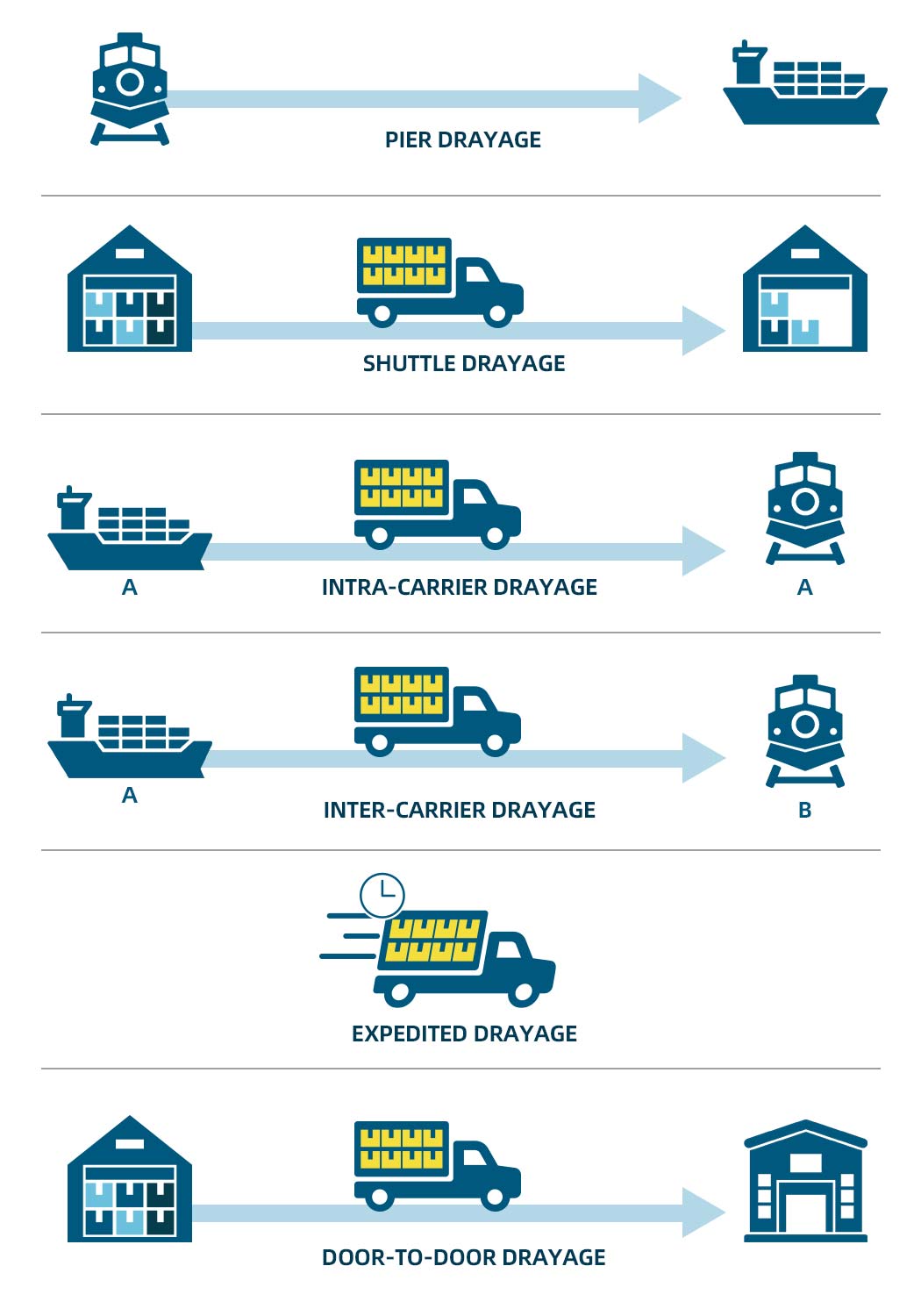
5. What are the Different Types of Drayage Services?
Different types of drayage services are developed to cater to the specific needs of all transportation modes, to facilitate the delivery process, or to make the most use of trucks. Below we will take a look at the meaning of six drayage service classifications. Learning about what types of drayage services there are will give you a better understanding of customized transportation solutions.
- Pier Drayage - The truck will transport goods from a rail hub to a pier or dock where the goods will be ready for loading onto a vessel.
- Intra-carrier Drayage - Intra-carrier drayage is used to transport goods within different transport hubs that belong to the same carrier. This type of drayage can play a better role when the goods are scheduled to board an airplane in another dock or when the goods have to be taken to the container freight station.
- Inter-carrier Drayage - With inter-carrier drayage, trucks will transport the goods between carriers. It can be used for intermodal transport: rail-to-sea, sea-to-rail, or rail-to-rail. For instance, trucks will carry the goods unloaded from vessels and then deliver the goods to start their scheduled railroad transport. The whole inter-carrier drayage process will be complete in the same region.
- Shuttle Drayage - Shuttle drayage can be used to store excessive freight containers. When docks lack space to hold containers, shuttle drayage trucks will become a fit option to keep the goods safe in storage until the next ship is prepared for departure.
- Expedited Drayage - Expedited drayage services will have the goods transferred in a quick, even urgent way. When there is a need for quick shipping solutions, expedited drayage will come into play. If you are shipping time-sensitive goods, expedited drayage services will be a better choice.
- Door-to-door Drayage - Using door-to-door drayage services means that the goods can be transported from a port to the final delivery address. Door-to-door drayage trucks will go directly to a customer.
6. What are Drayage Charges?
In most cases, drayage charges will include charges generated in the container picking-up process and the delivery process via trucking. To be more specific, the eventual amount of drayage fees can vary depending on the distance traveled, the container type, the cargo weight, and the pickup or delivery locations.
It is also worth mentioning that there are other types of fees associated with using drayage services, which can be referred to as accessorial charges. They include chassis fees, chassis-split fees, port congestion fees, overweight fees, flip fees, driver delay charges, pre-pull fees, drop fees, special handling charges, and more. Generally, the accessorial charges will be included in the overall drayages charges. Next, we will run you through the basics of the accessorial fees so you will know what makes up your bill.
- Flip Fees - If there is a need to pick up a container and mount it on a chassis, flip fees will be charged.
- Chassis Fees - Chassis fees incur from the utilization of a chassis to help move goods. Typically, a chassis will be offered by a third-party chassis owner, who will collect chassis fees from the cargo owner.
- Chassis-split Fees - Chassis-split fees are charged when a chassis is unavailable while the container is already unloaded and it requires the truck to retrieve it from another location.
- Drop Fees - When a truck delivers a container to a warehouse and then returns to pick up the empty container a while later, there will be drop fees.
- Pre-pull Fees - If there is a need to pick up a container from a port and store it inside a warehouse before delivery, pre-pull fees will be charged.
- Special Handling Charges - Special handling charges need to be paid when there are specific products: hazardous goods, fragile cargo, refrigerated freight, and more.
- Peak Surcharges - You need to cover peak surcharges if you transport shipments in peak times. For instance, when the trucking transportation takes place during weekends, holidays, or peak seasons, peak surcharges will incur. And you have to pay higher prices than off-peak times.
- Demurrage - Demurrage charges will incur when a container is held up at the port or terminal with the timeframe exceeding the allowed free time.
- Detention - Detention charges will incur when the equipment used to move containers is not returned to the port within the allowed free time.
7. How to Calculate Drayage Charges?
How the drayage pricing works may be a headache. Here let us break it down for you. Factors that can affect the drayage charges involve:
- ● the drayage rate per container or per move (The drayage rate varies depending on different drayage service providers )
- ● the distance from one location to another
- ● the time spent on delivering the freight
- ● the weight and size of the shipment
- ● whether there is a need to utilize special handling
- ● the equipment (a forklift, a pallet jack, ect.) required to move the freight
8. Six Effective Ways to Reduce Drayage Fees
In fact, drayage fees can be a reason for your mounting up shipping costs. Below are up to seven ways for you to cut back on drayage fees.
Proper Packaging
Maximize the space utilization when packaging your goods so that you can keep the overall weight low. Also, pay close attention to your product specifications to see if there is a need for special handling. The less special handling for your products, the simpler your packaging will be. And then you may pay less for the final drayage fees.
Consolidate the Shipments
Consolidating your shipments is another way to keep the freight weight light when possible. Compile your inventory together and deliver it as one shipment rather than multiple one-off small shipments.
Use Shipper-owned Containers
Using shipper-owned containers can effectively prevent unwanted fees such as demurrage and detention. Demurrage and detention charges may occur when the allotted free time ends.
Schedule Your Freight Shipping Accurately
Accurate pick-up and delivery times will ensure an efficient drayage. Be aware of delays because they can lead to additional costs, including demurrage and detention.
Separate Your Fragile and Non-fragile Goods
Fragile goods require special handling prior to shipping. And as we mentioned above, special handling will incur higher drayage fees. It is highly recommended to pack fragile and non-fragile goods separately. So the non-fragile goods can be delivered on crates or pallets in an easy and economical way.
Plan on Drayage Services in Advance
Planning on drayage services in advance when booking logistics services. And it will usually be cheaper than hurrying to arrange that in the last minute.




